READ: An Introduction to Hazardous Materials (Part 2 of 2)
/(4 RC) - This home study course is intended to provide interested members of the general public with a basic introduction to hazardous materials that can serve as a foundation for more specific research.
Read MoreREAD: An Introduction to Hazardous Materials (Part 1 of 2)
/(4 RC) - This home study course is intended to provide interested members of the general public with a basic introduction to hazardous materials that can serve as a foundation for more specific research.
Read MoreREAD: Respiratory Protection Program Toolkit Resources for Respirator Program Administrators (Part 2 of 2)
/(4 RC) - In order for respirators to provide effective protection they must be properly selected, used, and maintained as part of a written program, which describes how employers will provide employees adequate medical evaluations, training, and fit testing. This packet of informational documents, templates, and regulations contains all the necessary tools medical administrators need to develop an effective respiratory protection program.
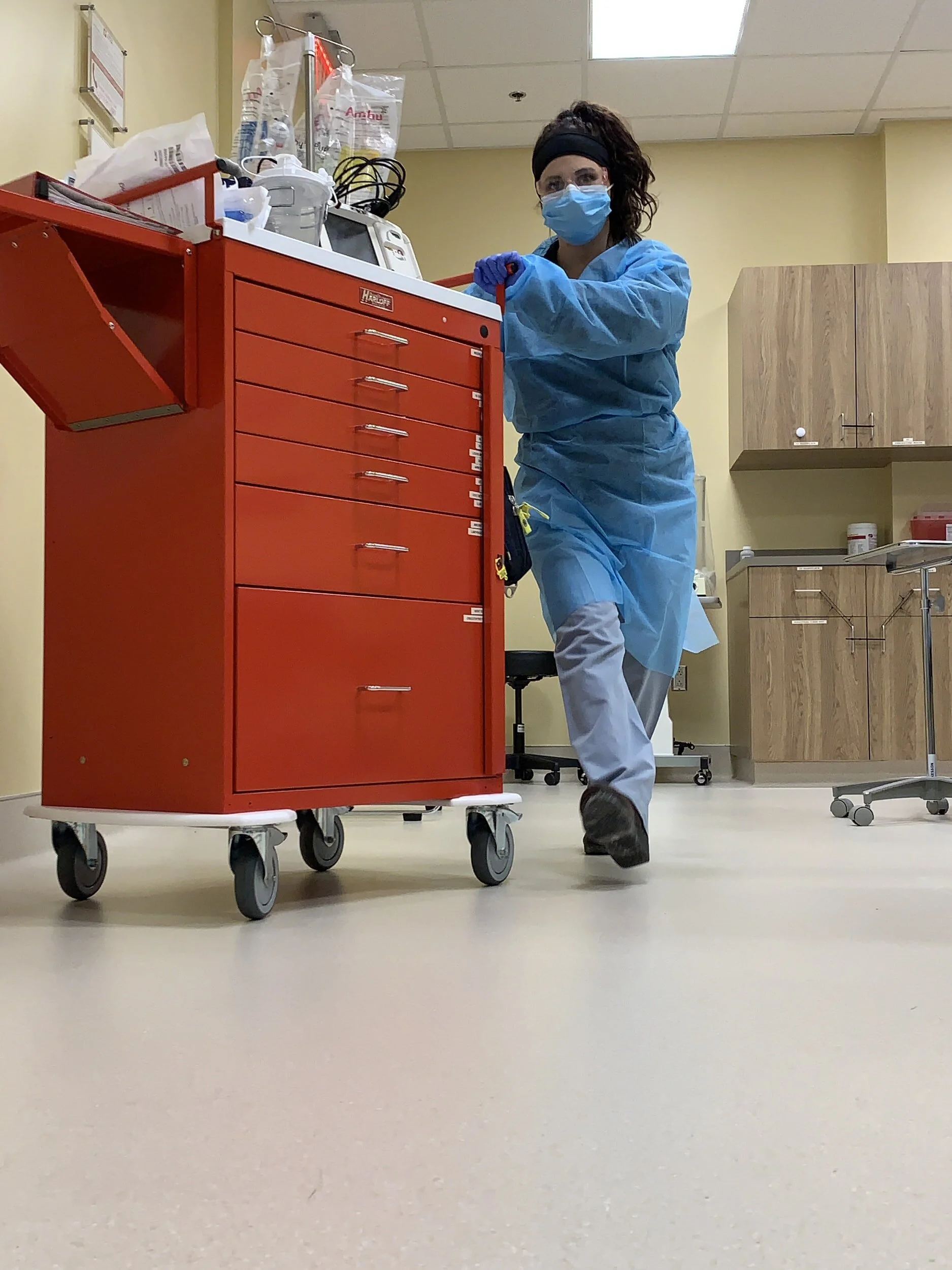
Read MoreREAD: Respiratory Protection Program Toolkit Resources for Respirator Program Administrators (Part 1 of 2)
/(4 RC) - In order for respirators to provide effective protection they must be properly selected, used, and maintained as part of a written program, which describes how employers will provide employees adequate medical evaluations, training, and fit testing. This packet of informational documents, templates, and regulations contains all the necessary tools medical administrators need to develop an effective respiratory protection program.
Read MoreREAD: OSHA - Controlling Silica Exposures in Construction (Part 2 of 2)
/(3 RC) - This guidance document addresses the control of employee exposures to respirable dust containing crystalline silica, which is known to cause silicosis, a serious lung disease, as well as increase the risk of lung cancer and other systemic diseases. This document provides information on the effectiveness of various engineering control approaches for several kinds of construction operations and equipment, and contains recommendations for work practices and respiratory protection, as appropriate.
Read MoreREAD: OSHA - Controlling Silica Exposures in Construction (Part 1 of 2)
/(3 RC) - This guidance document addresses the control of employee exposures to respirable dust containing crystalline silica, which is known to cause silicosis, a serious lung disease, as well as increase the risk of lung cancer and other systemic diseases. This document provides information on the effectiveness of various engineering control approaches for several kinds of construction operations and equipment, and contains recommendations for work practices and respiratory protection, as appropriate.
Read MoreREAD: OSHA Technical Manual - Section III, Chapters 1-7 (Part 4 of 4)
/(4 RC) - This collection of chapters from OSHA’s technical manual provides guidance on a variety of topics. The document covers advanced composites, indoor air quality investigation, ventilation investigation, heat stress, laser hazards, and Legionnaires’ Disease.
Read MoreREAD: OSHA Technical Manual - Section III, Chapters 1-7 (Part 3 of 4)
/(4 RC) - This collection of chapters from OSHA’s technical manual provides guidance on a variety of topics. The document covers advanced composites, indoor air quality investigation, ventilation investigation, heat stress, laser hazards, and Legionnaires’ Disease.
Read MoreREAD: OSHA Technical Manual - Section III, Chapters 1-7 (Part 2 of 4)
/(4 RC) - This collection of chapters from OSHA’s technical manual provides guidance on a variety of topics. The document covers advanced composites, indoor air quality investigation, ventilation investigation, heat stress, laser hazards, and Legionnaires’ Disease.
Read MoreREAD: OSHA Technical Manual - Section III, Chapters 1-7 (Part 1 of 4)
/(4 RC) - This collection of chapters from OSHA’s technical manual provides guidance on a variety of topics. The document covers advanced composites, indoor air quality investigation, ventilation investigation, heat stress, laser hazards, and Legionnaires’ Disease.
Read MoreREAD: OSHA Technical Manual - Section II, Chapters 1-4 (Part 3 of 3)
/(4 RC) - This collection of chapters from OSHA’s Technical Manual provides guidance for sampling air contaminants and assessing the extent of skin exposure. The document covers basic information related to air sampling, essential instructions for acquiring documented and valid exposure data, and guidance on the potential for skin exposure to chemicals in the workplace and the available means of assessing the extent of skin exposure. In addition, the document provides a broad overview of the types of equipment and instrumentation available for use by OSHA personnel, and an instruction guide for the handling, packaging, and shipping of industrial hygiene, safety, and construction samples.
Read MoreREAD: OSHA Technical Manual - Section II, Chapters 1-4 (Part 2 of 3)
/(1 RC) - This collection of chapters from OSHA’s Technical Manual provides guidance for sampling air contaminants and assessing the extent of skin exposure. The document covers basic information related to air sampling, essential instructions for acquiring documented and valid exposure data, and guidance on the potential for skin exposure to chemicals in the workplace and the available means of assessing the extent of skin exposure. In addition, the document provides a broad overview of the types of equipment and instrumentation available for use by OSHA personnel, and an instruction guide for the handling, packaging, and shipping of industrial hygiene, safety, and construction samples.
Read MoreREAD: OSHA - Silica Construction Regulation Text.
/(2 RC) - This document lays out the regulations for all occupational exposures to respirable crystalline silica in construction work. It provides specific exposure control methods for an extensive list of construction tasks involving crystalline silica.
Read MoreREAD: EPA Mold Web Course
/(4 RC) - This web course contains information on mold prevention and remediation. It is designed primarily for environmental and public health professionals.
Read More